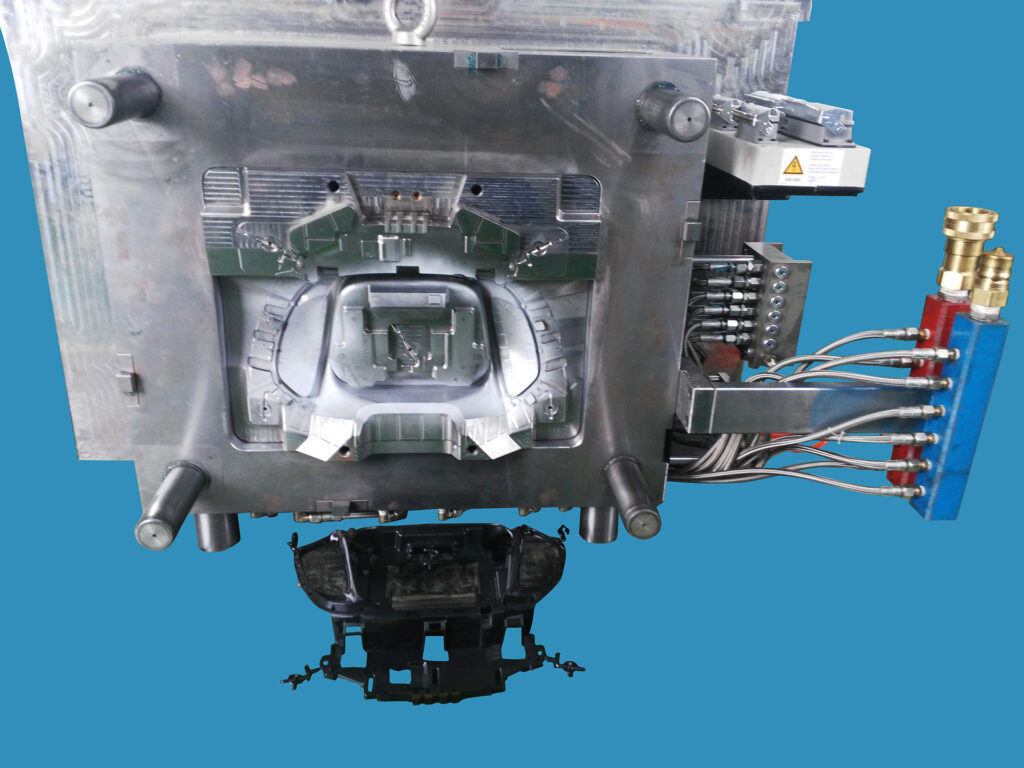
The global automotive industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by electrification, intelligent systems, and lightweight design. As vehicle architectures evolve, automotive injection molds have become a critical enabler of component quality, functional reliability, and scalable manufacturing.
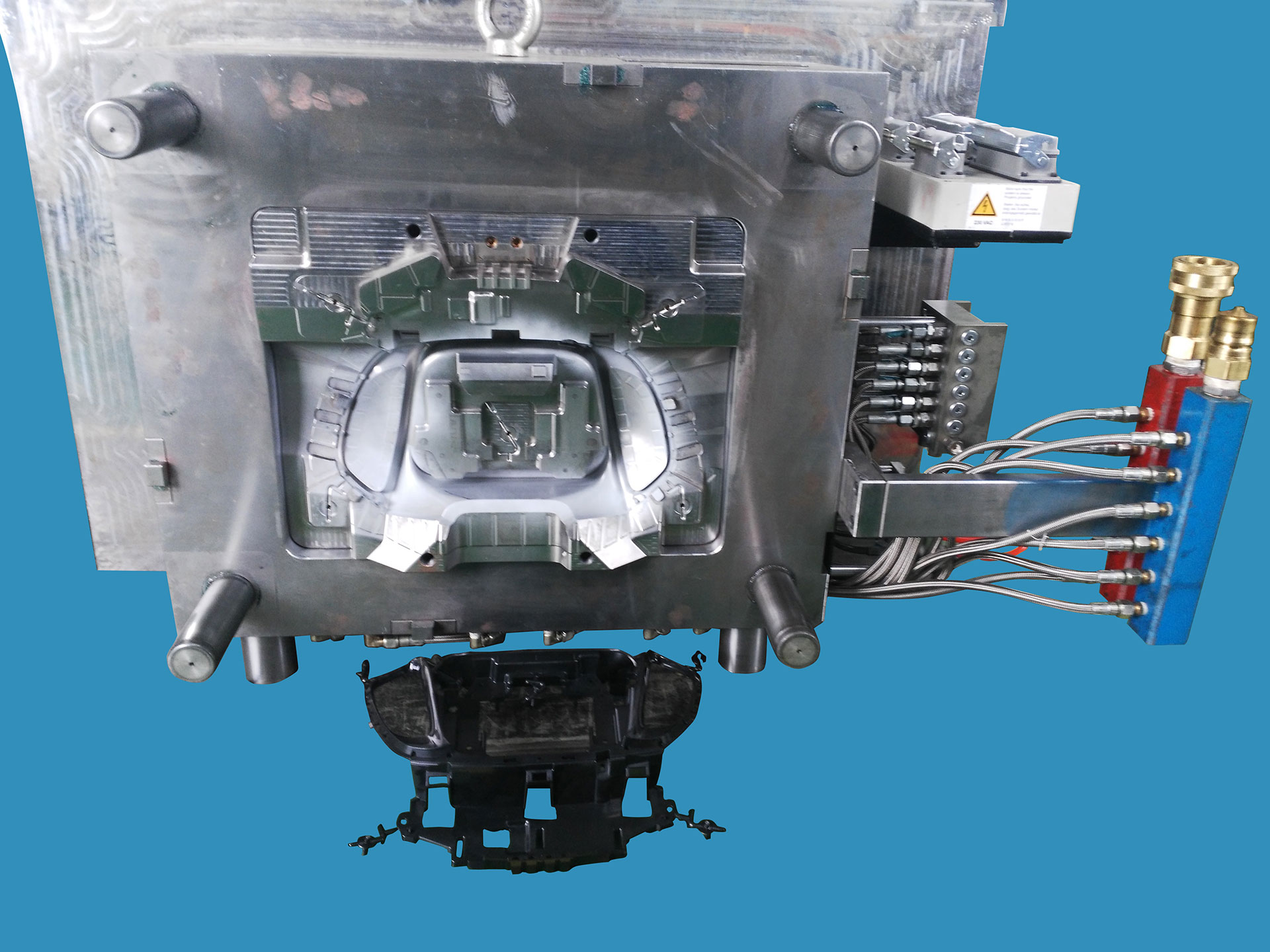
Far beyond basic tooling, injection molds determine dimensional accuracy, material performance, surface integrity, and production repeatability. For automakers and suppliers navigating tighter tolerances and shorter development cycles, mold engineering capability has become a key indicator of supply chain maturity.
1. Expanding Application Scope of Automotive Injection Molds
Automotive injection molds today support a far broader range of components than in previous decades. From conventional interior and exterior parts to high-precision functional components in new energy vehicles, mold complexity and performance expectations continue to increase.
Typical application areas include:
Interior Structural Components
Instrument panel structures, door panel clips, center console supports, and seat adjustment components, where low VOC performance, dimensional stability, and aesthetic quality are essential.
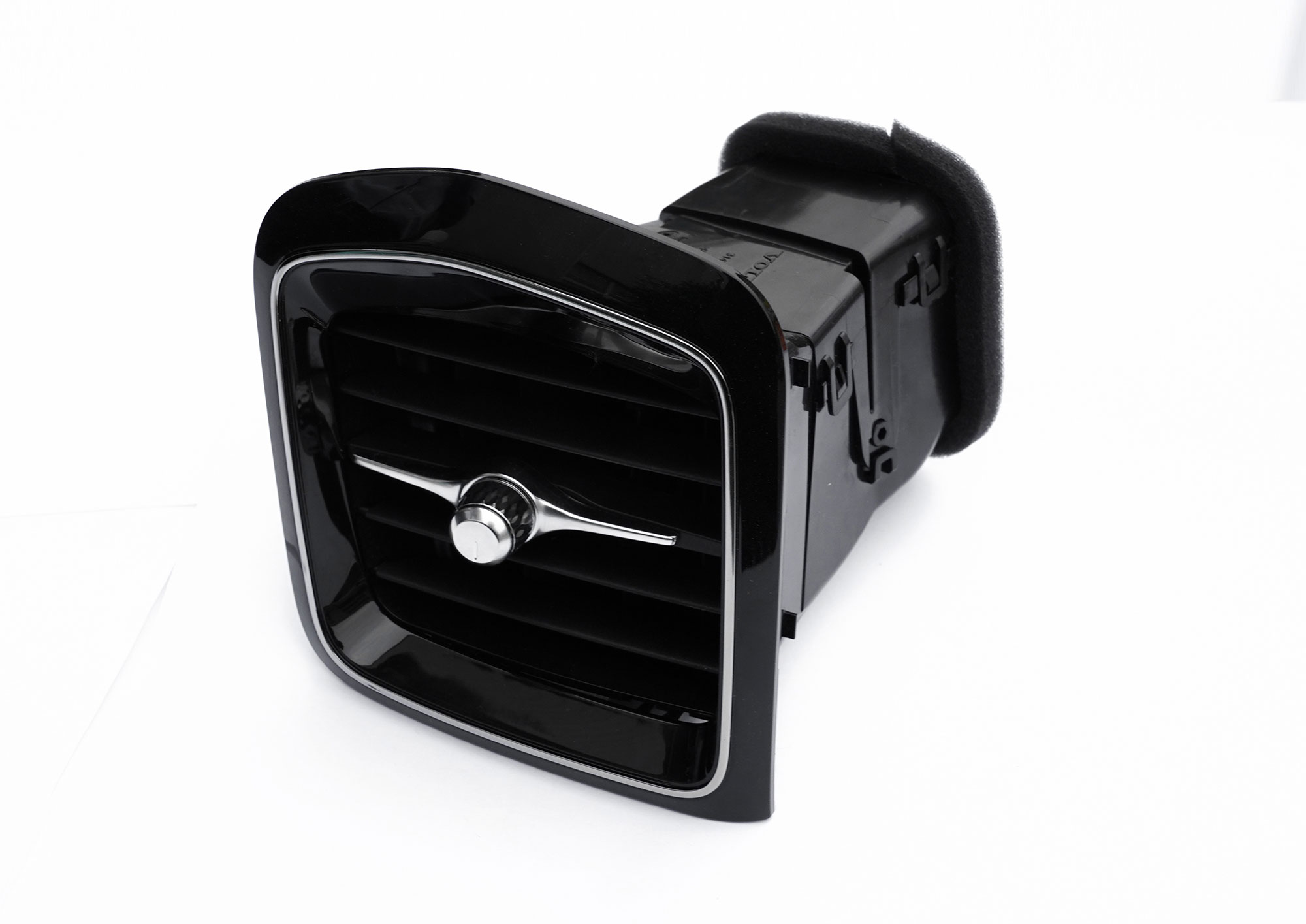
Exterior Plastic Components
Bumper brackets, mirror housings, grilles, and window guide systems that require UV resistance, impact strength, and long-term environmental durability.
Functional and New Energy Components
Electrical insulation parts, sensor housings, and plastic functional components used in electric motors, battery systems, and intelligent sensing modules. These parts often operate under higher thermal and mechanical stress than traditional automotive plastics.
Across these categories, manufacturers face common challenges: increasing part integration, thinner wall designs, reinforced polymers, and stricter consistency requirements for mass production.
2. Key Technical Drivers in Automotive Injection Mold Manufacturing
To meet evolving automotive requirements, injection mold manufacturing has shifted toward a more engineering-driven and system-oriented approach. Four technical areas are particularly decisive.
2.1 Front-End Engineering and Mold Design Validation
Mold design has moved upstream in the development process. Advanced CAD systems and mold flow analysis are now widely used to simulate filling behavior, cooling efficiency, shrinkage, and warpage before tooling is built.
This allows potential risks—such as deformation, sink marks, weld lines, and air traps—to be identified and mitigated early. Design optimization increasingly balances part quality with manufacturability, maintenance accessibility, and production efficiency.
2.2 Precision Machining and Consistency Control
Dimensional accuracy remains a defining requirement for automotive molds. Modern mold manufacturing relies on high-precision CNC machining, EDM, wire cutting, and surface grinding, supported by micron-level inspection systems.
For multi-cavity molds, cavity-to-cavity consistency is critical. Advanced positioning and synchronized machining techniques are now commonly applied to ensure stable, repeatable output across large production volumes.
2.3 Mold Steel Selection and Surface Engineering
Automotive molds must withstand high clamping forces, elevated temperatures, and frequent cycling. Mold steel selection is therefore closely linked to part material, reinforcement content, and expected production volume.
Commonly used mold steels include H13, S136, and pre-hardened grades such as 718H. In high-demand applications, surface treatments such as nitriding and PVD coatings are applied to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and mold life—often extending service life well beyond traditional expectations.
2.4 Mold Trial, Validation, and Process Optimization
Comprehensive mold trials are essential to ensure production readiness. Validation typically includes dimensional measurement, surface inspection, and functional testing using production-grade materials and parameters.
Effective mold manufacturers integrate trial results into rapid optimization cycles, refining mold structures, machining accuracy, and processing conditions to achieve stable, repeatable performance before mass production begins.
3. Quality Systems and Compliance in the Automotive Mold Supply Chain
As automotive platforms become more globalized, mold suppliers are increasingly evaluated on quality management and compliance capability. International standards such as IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 are now widely regarded as baseline requirements for participation in automotive supply chains.
Supporting these systems are in-house inspection laboratories equipped with coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), hardness testing, and environmental evaluation tools. These capabilities ensure that mold quality is verifiable, traceable, and consistent across projects and production sites.
4. Industry Practice: From Capability to Long-Term Partnership
In practice, leading automotive mold manufacturers distinguish themselves not only by equipment or certifications, but by their ability to translate engineering knowledge into predictable outcomes—shorter lead times, lower production risk, and long-term tooling stability.
Companies such as Idealmold, which have accumulated long-term experience in automotive injection mold projects, illustrate how systematic engineering processes, material expertise, and quality discipline contribute to reliable mold performance across diverse vehicle platforms.
Rather than acting solely as tooling suppliers, experienced mold manufacturers increasingly function as technical partners, supporting automakers and component suppliers throughout product development and lifecycle management.
5. Outlook: The Future of Automotive Injection Mold Manufacturing
As the automotive industry continues toward electrification and intelligent mobility, injection molds will face higher requirements for precision, durability, and development speed. Lightweight structures, integrated components, and advanced materials will further elevate technical thresholds.
In this environment, the competitiveness of automotive injection mold manufacturing will depend on engineering depth, process integration, and quality system maturity. Manufacturers capable of combining these elements will play a critical role in enabling stable, scalable, and high-quality automotive production worldwide.