In modern automotive design, interior plastics play a crucial role in defining the aesthetic appeal, comfort, and functionality of vehicles. From dashboards to door panels, consoles, and trim pieces, these materials are carefully selected to balance durability, safety, appearance, and cost. Understanding automotive interior plastic materials requires a deep dive into the types of plastics used, their properties, and the manufacturing processes that bring them to life.
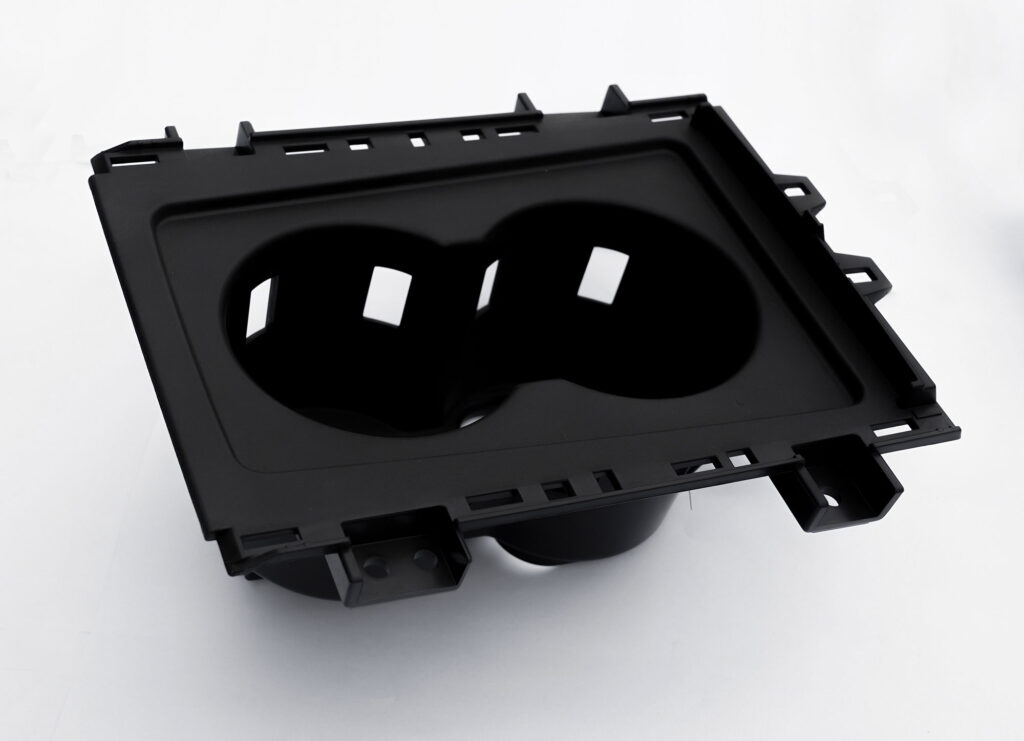

For companies and automotive manufacturers seeking custom solutions, Ideal specializes in custom injection molding of automotive components, offering tailored solutions for both small and large-scale production.
1. Common Automotive Interior Plastic Materials
Automotive interior plastics are not a single material; instead, engineers choose from a variety of plastics based on required properties. The most commonly used include:
1.1 Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Properties: High impact resistance, good surface finish, easy to paint or coat.
- Applications: Dashboard panels, center consoles, air vent frames.
- Why it’s used: ABS combines rigidity with toughness, providing durability while allowing design flexibility.
1.2 Polypropylene (PP)
- Properties: Lightweight, chemical and moisture resistant, low cost.
- Applications: Door panels, interior trim, seat components.
- Why it’s used: PP is highly moldable and offers good chemical resistance, making it suitable for frequently touched surfaces.
1.3 Polycarbonate (PC) and PC Blends
- Properties: High strength, transparency, heat resistance.
- Applications: Transparent or semi-transparent parts, instrument clusters.
- Why it’s used: PC is tough and provides excellent clarity, making it ideal for visible parts requiring high strength.
1.4 Polyurethane (PU)
- Properties: Flexible, soft-touch, abrasion resistant.
- Applications: Steering wheels, armrests, seat coverings.
- Why it’s used: PU provides a premium feel while offering durability, comfort, and resistance to wear.
1.5 Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE/TPV)
- Properties: Soft-touch, elastic, impact-resistant.
- Applications: Gaskets, seals, flexible trim.
- Why it’s used: TPEs combine rubber-like elasticity with thermoplastic processability, making them ideal for functional and decorative purposes.
2. Key Material Considerations
When selecting automotive interior plastics, manufacturers must balance several key factors:
- Safety: Materials must be flame-retardant and low in toxic emissions (complying with regulations like FMVSS 302 or ISO 3795).
- Durability: UV, heat, and scratch resistance are critical for parts exposed to sunlight and regular use.
- Aesthetics: Texture, color stability, and paint adhesion determine the overall interior appeal.
- Cost and Weight: Lightweight materials like PP reduce fuel consumption and overall cost.
- Recyclability: Increasingly, manufacturers focus on sustainable materials to reduce environmental impact.
Ideal assists automotive manufacturers in selecting the optimal materials for each application, ensuring that each part meets both performance standards and aesthetic requirements.
3. Manufacturing Processes for Interior Plastics
The choice of manufacturing process is closely linked to material properties, production volume, and part complexity. Ideal leverages advanced injection molding technology to provide precise and consistent production for a wide range of interior components.
3.1 Injection Molding
- Description: Molten plastic is injected into a mold under high pressure.
- Suitable Materials: ABS, PP, PC, TPE.
- Advantages: High precision, mass production capability, complex geometries.
- Common Applications: Dashboards, door panels, console components.
- Ideal Advantage: Our custom molds allow for rapid prototyping and scalable production, ensuring clients’ designs are realized with high accuracy.
3.2 Thermoforming
- Description: A plastic sheet is heated and shaped over a mold using vacuum or pressure.
- Suitable Materials: ABS, PC, PP blends.
- Advantages: Ideal for large, shallow parts; cost-effective for medium volumes.
- Common Applications: Instrument panel skins, interior trim covers.
3.3 Extrusion
- Description: Plastic is forced through a die to create long, continuous shapes.
- Suitable Materials: PP, TPE.
- Advantages: Continuous production, excellent for seals, trim, and gaskets.
- Common Applications: Door seals, window trims, cable conduits.
3.4 Coating and Painting
- Purpose: Enhance surface aesthetics, improve scratch and UV resistance.
- Techniques: Spray coating, vacuum metallization, hydrographics.
- Common Applications: Dashboard decorative panels, center consoles, air vents.
- Ideal Advantage: Our coating and finishing processes ensure consistent quality and premium appearance, meeting both OEM and aftermarket requirements.
4. Trends and Innovations
The automotive interior plastic sector is evolving rapidly:
- Lightweighting: High-performance composites and blends reduce vehicle weight.
- Soft-touch and multi-material molding: Combining hard and soft plastics in a single part enhances feel and ergonomics.
- Sustainability: Increasing use of recycled plastics and bio-based polymers.
- Smart Surfaces: Integration of touch-sensitive controls and embedded electronics.
Ideal stays ahead of industry trends, offering innovative solutions such as multi-material injection molding and eco-friendly material selection, ensuring clients remain competitive in a rapidly changing market.
5. Conclusion
Automotive interior plastics are far more than simple materials; they are carefully engineered components that balance safety, aesthetics, functionality, and cost. From ABS dashboards to TPE gaskets, understanding both material properties and manufacturing processes is crucial for designers, engineers, and suppliers.
With Ideal’s expertise in custom injection molding, automotive manufacturers can achieve precise, high-quality, and durable interior components tailored to their specific designs. As consumer expectations evolve and sustainability becomes paramount, the right material and manufacturing partner can make all the difference.
References
- ISO 3795: Road vehicles — Measurement of flammability of interior materials
- FMVSS 302: Flammability of interior materials
- Automotive Interior Materials Handbook, Elsevier, 2020
- “Plastics in Automotive Interiors: Material Selection and Processing”, SAE Technical Paper, 2018